Binomial Heap
Binomial Heap是由一群 Binomail Tree所組成的 Binomial Tree(BT)含有下列特性
- 高度為k的 BT共有2^k個node
- 高度為k的 BT可以看成 BT0~BTk-1的組合 再加上一個root組成
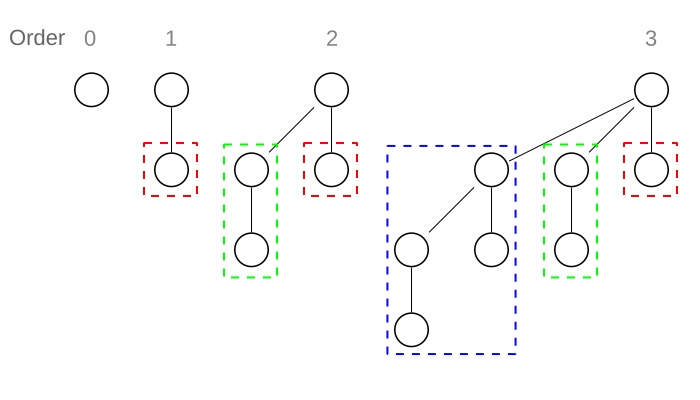
Binomial Heap
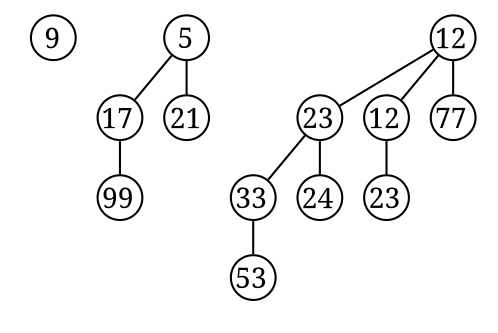
- 是 mergable heap
- 由一群 Binomial Tree組成,每個BT都滿足 min-heap的性質
- 對於高度為k的BT只能存在最多一棵
- 以二進位來看待的話,第K位就代表是否存在高度為K的BT
- 以下圖為例,就是11001 (右邊最小)
- 因此任何數量的結點都可以用不同的BT給組合出來
##Implement##
- 採用 Left-Child Right-sibling的方式來實現,左邊指向child,右邊指向同輩
- value: node的值
- degree: 以此node為root的BT的高度
- parent: 指向其parent

class Node{
public:
Node* parent;
Node* child;
Node* sibling;
int value;
int degree;
Node(){
parent = NULL;
child = NULL;
sibling = NULL;
value = 0;
degree = 0;
}
};
##Functions##
- getMin
- size
- Travese (postorder)
- mergeHeap
- Insert
- deleteMin
##getMin## 由於每個BT本身都已經是min-heap的特性了,因此只要針對每個BT的root比較其值即可
int getMin(){
Node* x = head;
int min = INT_MAX;
while(x!=NULL){
if(x->value < min)
min = x->value;
x = x->sibling;
}
return min;
}
##size## 由於 Binomial Heap內都是由 Binomial Tree組成,所以可以由每個BT的degree得到其node數量 再把所有加總即可。
int size(){
Node* tmp = head;
int count=0;
while(tmp){
count+= (1<<tmp->degree); // 2^degree
tmp = tmp->sibling;
}
return count;
}
##Postorder## 這邊是每個BT都要獨立跑一次Postorder的結果,所以在遞迴的過程中要對root做一些控制
//對每一棵BT都跑一次postorder
void postorder(){
Node* tmp = head;
while(tmp){
_postorder(tmp);
tmp = tmp->sibling;
}
printf("\n");
}
//用parent判斷是不是root,避免root跑去呼叫到別的BT
void _postorder(Node* node){
if(!node)
return;
_postorder(node->child);
if(node->parent)
_postorder(node->sibling);
printf("%d ",node->value);
}
##MergeHeap## 要合併兩個 Binomial Heap
- 先把兩個 Binomail Heap的 BT list給重新串接起來,以degree為key做sorting.
- 再根據這個新的BT list開始進行一系列的合併
- 如果只有兩個高度相同的BT,就直接合併
- 如果有三個高度相同的BT,就把後面兩棵合併(維持sorting)
void MergeHeap(BinomialHeap &bh){
mergeHeap(bh); //先把BT list給重新串接起來
Node* prev = NULL;
Node* x = head;
Node* next = x->sibling;
while(next){
if( (x->degree != next->degree) || next->sibling && next->sibling->degree == x->degree){
prev = x; //前後兩棵BT的高度不同 或是 後面三棵BT的高度都相同
x = next; //那就把指標往前移動,下次再合併
}
else if( x->value <= next->value){ //前面BT的值比較小,所以後面的合併進來
x->sibling = next->sibling;
mergeTree(next,x);
}
else{ //前面那棵BT的值比較大,要往後合併,視情況也要更新 head指標
if(!prev){
head = next; //更新head 指標
}
else{
prev->sibling = next;
}
mergeTree(x,next); //合併
x = next;
}
next = next->sibling;
}
}
要把兩個 Binomial Heap的BT list給重新串接起來,採用 merge sort的方法

- 使用 newHead紀錄合併後的頭
- 使用 newCurr來紀錄每次合併後的尾
void mergeHeap(BinomialHeap &bh){
Node* head2 = bh.head;
Node* head1 = head;
Node* newHead, *newCurr;
if(!head1){ //如果本身是空的,就不需要合併,直接指向對方即可
head = head2;
return ;
}
else if(!head2){ //對方是空的,也不需要合併
return ;
}
//先行尋找誰的開頭比較小,當做新串列的頭
if(head1->degree > head2->degree){
newHead = newCurr = head2;
head2 = head2->sibling;
}
else {
newHead = newCurr = head1;
head1 = head1->sibling;
}
while(head1 && head2){
if(head1->degree < head2->degree){
newCurr->sibling = head1;
newCurr = head1;
head1 = head1->sibling;
}
else {
newCurr->sibling = head2;
newCurr = head2;
head2 = head2->sibling;
}
}
while(head1){
newCurr->sibling = head1;
newCurr = head1;
head1 = head1->sibling;
}
while(head2){
newCurr->sibling = head2;
newCurr = head2;
head2 = head2->sibling;
}
head = newHead;
}
合併兩個 Binomial Tree,由於我們是min-heap的特性,所以當兩棵高度相等的BT要合併時,根據root的值來決定誰是合併後的root.
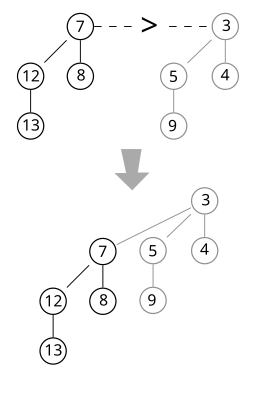
假設已經知道BT(y)的值比BT(z)還要大,所以BT(z)會是合併後的root
- y的parent指到z
- y的sibling 指到 z本來的child
- z的child 指到y
- z的degree 加一
void mergeTree(Node* y,Node* z){
y->parent = z;
y->sibling = z->child;
z->child = y;
z->degree++;
}
##Insert## 要插入一個新的元素,就是創見一個新的 Binomial Heap,然後跟原本的Heap執行合併即可
void insert(int value){
BinomialHeap bh;
bh.head = new Node();
bh.head->value = value;
MergeHeap(bh);
}
##Delete## 要從 BinomialHeap中刪除當前最小元素
- 先找到最小元素所在的那棵BT
- 把該BT從list裡面拔除
- 把該BT的children給反向排序(degree為key)
- 在跟原本的BT list合併

void deleteMin(){
int min = head->value;
Node* tmp = head;
Node* minPre = NULL;
Node* minCurr = head;
// 找到最小的node位於何處,由於要將該BT給拔除,所以必須要記得該BT前面那棵BT
// 如果最小棵的是第一棵,那也要一併更新 head 指標
while(tmp->sibling){
if(tmp->sibling->value < min){
min = tmp->sibling->value;
minPre = tmp;
minCurr = tmp->sibling;
}
tmp = tmp->sibling;
}
if(!minPre && minCurr) //最小棵是第一個
head = minCurr->sibling;
else if(minPre && minCurr)
minPre->sibling = minCurr->sibling;
//H' Make-BINOMIAL-HEAP()
Node *pre,*curr;
//用三個指標反轉一個 single link list
pre = tmp = NULL;
curr = minCurr->child;
while(curr){
tmp = curr->sibling;
curr->sibling = pre;
curr->parent = NULL;
pre = curr;
curr = tmp;
}
//創建一棵新的binomial heap,並且讓他的head 指向反轉後的BT list
BinomialHeap bh ;
bh.head = pre;
//再度合併
MergeHeap(bh);
}
圖片來自
- Binomial Wiki
- Introduction To Algorithms,Chapter 19 Binomial Heaps